Preparation and application of DBU
Preparation and application of DBU
Background and Overview
DBU: 1,8-diazabicyclo bicyclic (5,4,0) – 7-undecene, a bicyclic amidine compound with strong alkalinity. An article published on nature in 2005 said that DBU, as a convertible polar solvent and extractant, can be used in the extraction of oils and fats. The extraction rate is high. During the separation process, only CO2 is needed to make the polarity of the converted ionic liquid higher, so that the oil layer can be separated from the ionic liquid layer. Then, N2 can be introduced into the ionic liquid layer to discharge and reduce the polarity, so that it can be recycled. As a strong organic base with unique structure, DBU has been applied in many synthesis reactions, showing that other strong bases are difficult to play a catalytic role. DBU has the characteristics of mild reaction conditions, simplified synthesis steps, high selectivity and yield of products. It can be predicted that with the deepening of people’s understanding of DBU, DBU will be widely used in the research of improving the existing synthesis process, developing new organic synthesis methods, and synthesizing new products.
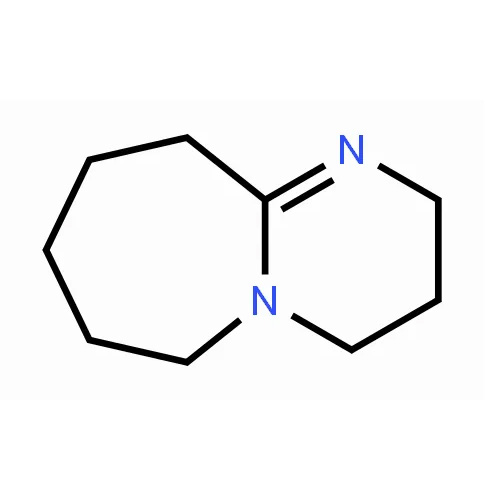
Chinese name 1,8-diazabicycloundecen-7-ene Chemical formula C9H16N2
Foreign name 1,8-Diazabicyclo [5.4.0] undec-7-ene (DBU) molecular weight 152.24
CAS Registration No. 6674-22-2 CAS Registration No. 6674-22-2
preparation
The general method for synthesizing DBU is nucleophilic addition of caprolactam and acrylonitrile to generate N – (2-cyanoethyl) caprolactam, catalytic hydrogenation to obtain N – (3-aminopropyl) caprolactam, dehydration and cyclization to obtain DBU. When synthesizing N – (3-aminopropyl) caprolactam, generally no solvent is used, the operation is simple, but it is difficult to control the reaction temperature, and a large number of polymers are often produced. When synthesizing DBU, catalytic hydrogenation is usually required under pressure, which requires high reaction equipment.
application
DBU is a strong alkaline reagent, but it is a weak nucleophilic reagent, which is easy to combine with protons but not with carbon atoms. Therefore, DBU is mainly used as a strong alkaline reagent to transfer protons and play the role of base or catalyst. The characteristic of DBU participating in the reaction is that it generally requires the amount of DBU of other substances, and the applied reactions are mainly focused on some reactions with proton transfer, such as elimination, isomerization, addition, esterification, etherification, amidation, diazotization, etc.
-
Eliminate reaction
DBU has been used in a variety of elimination reactions to introduce unsaturated bonds into reagent molecules. As an intermediate and raw material of organic synthesis, just a few examples are enough to show the application of DBU in elimination reactions.
1) Elimination of hydrogen halide by halogenated alkanes
A typical reaction is that 1,1-diiodobutane and DBU of the same amount of substances are heated and refluxed together to produce a brown solid, and the product (E) – 1-iodo-1-butene is obtained by distillation and separation from the reaction mixture, with a yield of 80%. Generally, it is difficult for DBU to dehydrohalogenate vinyl halides to generate alkynes, but (E) – vinyl bromide and DBU with special structure reflow in benzene and almost quantitatively convert into corresponding alkynes, while (Z) – isomers cannot undergo such reactions. There are many examples of dehydrohalogenation of halogenated hydrocarbons with DBU, which is sufficient to show that DBU is a very effective dehydrohalogenation reagent for halogenated alkanes.
2) Elimination of hydrogen halide by N-haloamide
Under the action of DBU, N-haloamide can smoothly remove hydrogen halide, and then rearrange to isocyanate. N-chlorobenzamide can rearrange to obtain benzene isocyanate under the action of DBU, with a yield of more than 90%. It is difficult to obtain phenyl isocyanate by replacing DBU with organic base such as triethylamine.
-
Isomerization reaction
Double bond isomerization and epimerization are extremely useful in organic synthesis, and DBU has a good catalytic effect in this isomerization reaction.
1) Double bond isomerization
The DBU can be used to β,γ- Unsaturated ester compounds are converted into corresponding α,β- Unsaturated ester. Under the action of DBU, 60% of 3-pentenoic acid esters form stable 2-pentenoic acid esters; Under the action of catalyst DBU, β,γ- Unsaturated nitriles can also form stable α,β- Unsaturated nitrile.
2) Epimerization reaction
The stereoisomer mixture reacts with DBU at room temperature for 1h, and its cis – 3,4 isomer is converted into trans – 3,4 isomer, with a selectivity of 96%. This provides a method for the synthesis of compounds with special configurations.
-
DBU as alkaline reagent α- Reaction of H producing carbonic anion intermediate
DBU is to make α- It is an alkaline reagent for hydrogen compounds to remove protons and form carbon negative ions, among which Michael addition reaction is the most typical, with mild reaction conditions and few side reactions. In the reaction of cyclohexanone formate and methyl acrylate, DBU was used as basic reagent to obtain the product with a yield of 96%.
DBU makes the nitro compound Michael react with the styrene ketone containing double bond, and the yield is 95%; Compound 15 reacts with 2-cyclopentenone via Michael reaction, and generates (+) – 3-cyclopentenone acetic acid after hydrolysis and decarboxylation. The total yield is 43% and the optical purity is 96%. Although the yield of the product obtained by using triphenyllithium or potassium tert butoxyl as catalyst is close, the optical purity is much lower, only 7%~76%. In addition, in Knovenagel condensation reaction between malonic acid and hexanal, DBU was used as basic reagent, and the reaction was conducted at 90 ℃ for 10h to obtain β,γ- The selectivity of unsaturated isomers is 94%, and the yield is 56%.
-
Esterification, etherification and amidation reaction
DBU can be used as a catalyst to prepare esters and amine compounds from carboxylic acids and halohydrocarbons, and to prepare ethers, esters, carbamates and other compounds from alcohols. This type of reaction is prepared by deprotonation of carboxylic acid or alcohol with alkyl halides, acylation agents or other electrophilic reagents. Esterification and amidation reactions are generally conducted at room temperature, while etherification reactions are generally conducted at 60-80 ℃.
-
Cycloaddition reaction
In the synthesis of 2,5-dimethyl-3-phenyl-2-cyclopentenone, DBU was used as catalyst, and the yield reached 70%. In the synthesis of tetrahydropyrrole derivatives, DBU is also used as a catalyst for cycloaddition, and the yield is more than 90%.
-
diazotization reaction
![1-8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene,DBU catalyst,CAS 6674-22-2](https://www.dbuchem.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/logo2.png)

